Conservation means maintaining or protecting something so that it is not wasted or lost.
Water conservation is maintaining water as a natural resource and ensuring that the water is not lost but is available for our use.
If water is not conserved, then it leads to scarcity or shortage of water.
Harvesting is the collection of rainwater by trapping it from the roofs of houses, rocks, and trees.
Rainfall brings clean and uncontaminated water that should be trapped and stored.
Harvesting of rainwater can be done in various ways for example:
A system of gutters is built around the house to meet at one collection point, the storage tank. In this case, the material used in making the roof must be safe and clean. For instance, asbestos roofing is said to make rainwater unfit for human consumption because one can easily get cancer. Painted roofs may contribute to lead poisoning in humans from the paint which may contain lead.
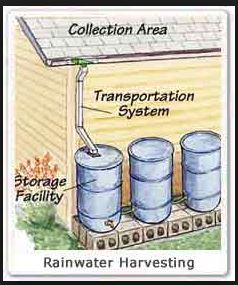
A tree has many leaves and branches. Rainwater falls on the leaves and branches and flows down in little streams along the stem to the ground where it is lost when it soaks into the ground.
This water can be collected and trapped in a container by using some kind of gutters made from iron sheets, tins or even the hard polythene or plastic material.

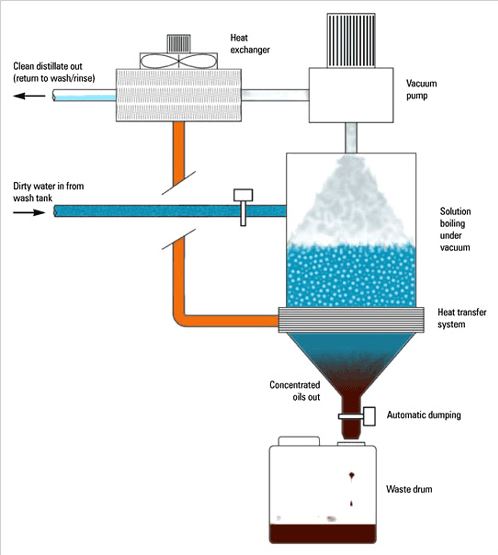
Water that has been used in one way or another and has become dirty can be used again after it is treated. Recycling water is treating used water so that it becomes safe and able to be used yet again. This ensures that polluted water is treated and instead of letting the water get lost, it is used again. This method is often used in urban areas. Look at the image below:
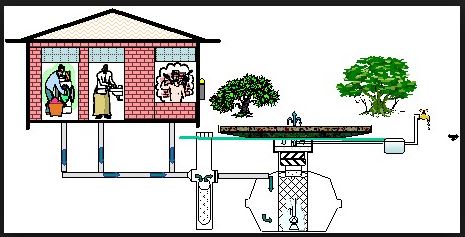
- A given amount of water can be used for one task and then used for yet another task without the need to treat it. This is called re-using. An example is when water is used to clean and rinse clothes after which the remaining water is used to clean the floor of houses or sprinkled on dusty paths to hold dust, or used to wash a car.
- When generating hydroelectric power, water is passed through a special tunnel in order to turn turbines which in turn move generators that produce electricity.
- After electricity is produced, the water rejoins the river downstream where it can be used for agricultural irrigation, bathing, and other domestic chores.
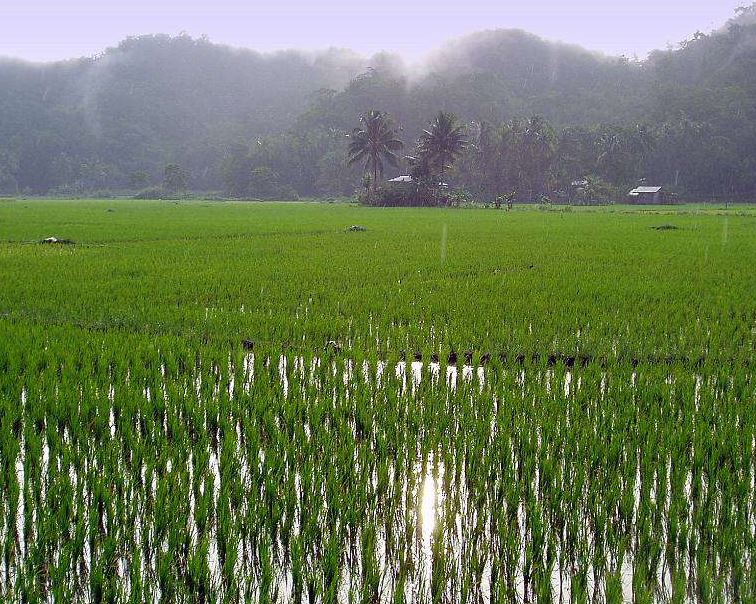
There are many types of irrigation, depending on how the water is supplied to
the plants.
In flood irrigation (used in rice farming), water is allowed into a paddock of rice to cover the entire piece to a certain depth. In overhead irrigation, the water gets to the plants from above, for instance by use of sprinklers.

In drip irrigation, each individual plant is fed with the water directly at the roots, drop by drop.

In overhead irrigation, all the water used does not fall on the plants, therefore, some go to waste.
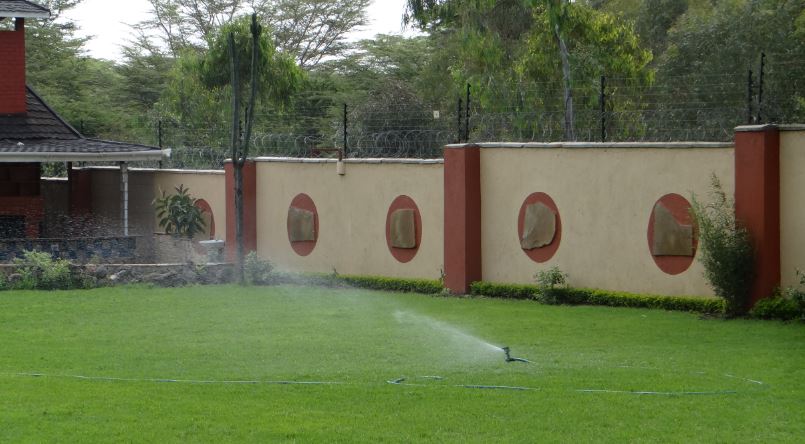

In drip irrigation, only a small amount is used and used very efficiently to ensure the plants absorb most of the water. Very little or none at the most efficient and effective method of water conservation in irrigation.

Mulch is the name given to the organic material used to cover the soil around plants to avoid loss of water from the ground. Plant materials such as grass can be used as mulch. A shed can be built for
young seedlings to keep away intense sunlight. Mulching and shading are
water conservation methods that reduce the evaporation of water from the soil to the atmosphere. This ensures that water is used by plants rather than getting lost or wasted through evaporation.

One way of ensuring the water in the rivers during the rainy season is kept for future use is storing it. This becomes a store of water that harvests and retains water for use for domestic purposes or for crop and livestock use. Dams can be built in areas where floods occur to conserve the water by storing excess water. Dams can also be built-in dry areas so that water can be collected and stored during the wet season for use in the dry season. Dams are also called reservoirs.

1. The flow chart below shows a large scale water treatment process.
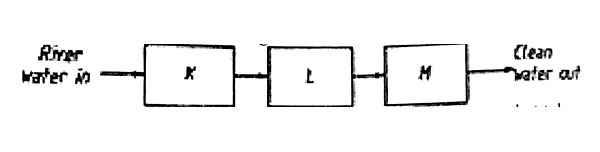
Which one of the following gives the correct order of processes that take place at K, L, and M?
A. Sedimentation, filtration, Chlorination
B. Filtration, Sedimentation, Chlorination
C. Sedimentation, Chlorination, Filtration
D. Chlorination, Sedimentation, Filtration
2. In which one of the following types of irrigation is water used most economically?
A. Sprinkle irrigation B. Flood irrigation
C. Drip irrigation D. Basin irrigation
3. The most convenient method of distributing water from a dam to various livestock fields in a farm is by
A. Transportation using tractors
B. Pumping and piping
C. Transporting using work animals
D. Channeling through furrows
4. Mulching helps in the conservation of water for crop growth by
A. Reducing the rate of evaporation from the soil
B. Absorbing rainwater and releasing it slowly to the crops
C. Preventing weeds from absorbing water from the soil
D. Preventing rainwater from sinking into the lower layers of the soil.
5. I, II, and III in the diagram below represents processes involved in a simple water cycle.
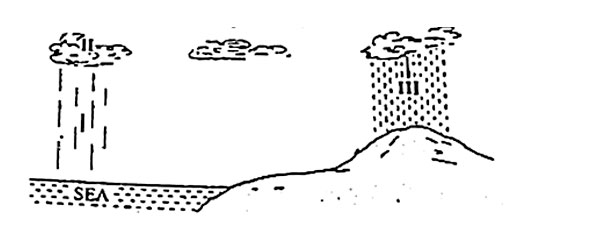
Choose the correct order of processes represented by I, II and III.
|
I |
II |
III |
| A. Condensation |
Evaporation |
Precipitation |
| B. Evaporation |
Condensation |
Precipitation |
| C. Evaporation |
Precipitation |
Condensation |
| D. Condensation |
Precipitation |
evaporation |
6. Which one of the following sources of water would most likely supply a farmer with relatively clean and safe water?
A. Lakes B. Rivers C. Dams D. Springs
7. Which one of the following farming practices is most effective in conserving moisture in the soil?
A. Strip cropping B. Terracing C. Mulching D. Contour cultivation
8. Which one of the following is a CORRECT statement about sprinkler and drip irrigation?
A. Water loss through evaporation is higher in drip irrigation than in sprinkler irrigation.
B. Sprinkler irrigation is more suitable in areas where water is scarce than drip irrigation.
C. Drip irrigation encourages the growth of more weeds than sprinkler irrigation.
D. More water is used in sprinkler irrigation than in drip irrigation on the same size of land.