| Grazing method |
|---|
6
Grazing is the direct use of pastures by livestock.

The different methods of grazing are:
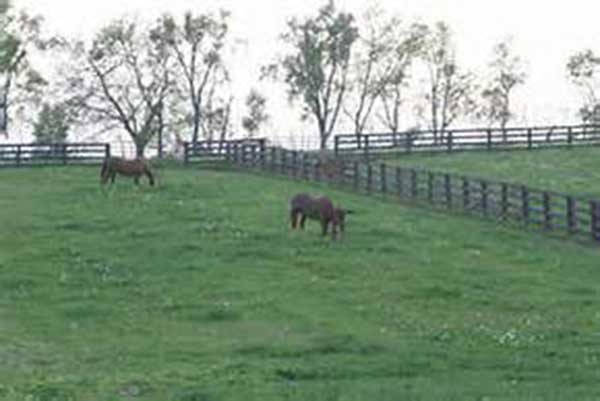
In this type of grazing, the farmer guides the animals to where good pasture and water sources are available. The animals get good attention and care.

1. No huge expenses for fencing or water supply
2. One herdsperson can look after hundreds of animals. the labor cost is redued.
3. Animals are free to move about so they have plenty of exercise
4. The farmer doesn’t have to own a lot of land. Pasture can be rented for use for an agreed period
5. Animals get to eat a variety of natural pastures
1. Diseases are easily spread among the animals in a herd because they are always close together
2. Animals may mix with other herds, which may cause spread of diseases
3. The animals may sometimes be very far from veterinary services
4. The herdsperson has to travel over long distances. this can be very tiring
Zero grazing is also called stall-feeding. The animals are kept in an animal house called a stall. The farmer harvests the pasture or fodder and takes it to the animal. It is very popular in keeping dairy cows for milk. It is common in areas where shambas are small.
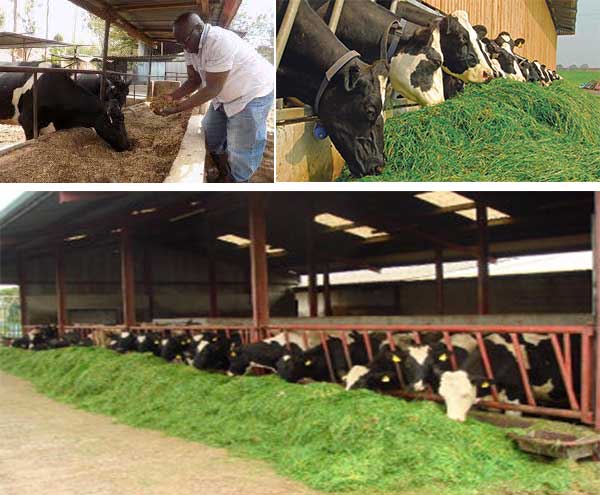

1. Livestock cannot get disease easily since their movement is limited
2. The feeds are used to the maximum
3. Many animals can be fed from a very small area
4. Manure is easily collected since it is in one place.
5. Animals can be observed from close quarters
6. The animals are more productive.
1. Diseases can easily spread to animals in the same enclosure because stalls might be too close
2.It is expensive to start because stalls have to be built
3.Requires a lot of labor, especially in planting, caring, harvesting and transporting feeds
4. Due to limited movement, animals do not have the chance to exercise.
In rotational grazing the piece of land is divided into portions or padocks. The animals are then moved from one portion to another once the pasture is eaten to a restricted level in a given portion. In each portion, a water source must be conveniently located.
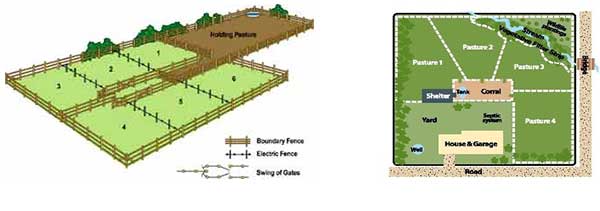
1. Helps to control livestock diseases
2. Allows time for the pasture to grow during the rest period
3. Pasture in the rest areas can be harvested for future use
4. Pests are controlled
1. Expensive because the farmer has to build fences and provide water in all paddocks
2.Can’t be used by a farmer with many animals
6
The types of rotational grazing are tethering strip grazing and paddocking or paddock grazing.
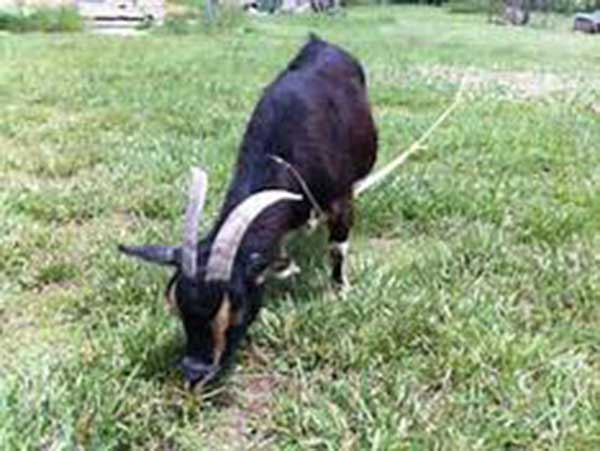

An animal is tied or tethered to a post, a peg or a tree.
1. Requires less labor
2. Expensive fencing is not necessary
3. Very good use of pasture because grazing is carefully controlled.
1. The animal can choke on the ropes if poorly teethered
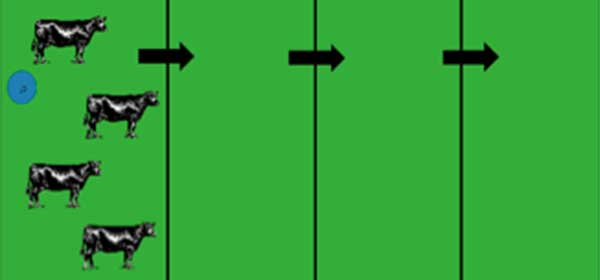
Animals are kept on strips of land. The fence is moved once the animals have eaten all the pasture on the strip of land.
1. Maximum use of pasture can be achieved
2. There is no need to spend money on expensive fences
3. Excess pasture can be harvested and stored
1. You need to have very high quality and well maintained pasture so that animals have most nutrients
Animals are kept within a fenced area called a paddock.
1. Allows for harvesting and storage of pasture
2. Requires a small piece of land
1. It is expensive to establish the paddocks and supply water
2. Can only be used with a few animals
