Interdependence is a relationship where organisms depend on each other for something that is needed for their survival.
A mosquito shortly after sucking blood from a human being
An organism that depends on and benefits from another is a parasitic organism or a parasite.
The organism that it depends on is the host.
In this kind of relationship,the parasite benefits while the host does not, in fact the host may experience ill health or disease and may finally die.
Interdependence can exist between:
• a plant and another plant
• a plant and an animal
• an animal and another animal
Now, let’s learn more about these categories
This category or class of interdependence is the situation when one plant relies on another plant survival.
This means that both the parasite and the host are plants.
Cases of interdependence between plants occur for various reasons.
These reasons include:
Some plants have weak stems.
For these plants to reach sunlight, they have to rely or depend on other plants with stronger stems.
These plants with weaker stems develop some features, which they use to attach themselves to the more rigid or stronger plants.
A plant like the passion plant which produces passion fruit has tendrils which it uses to firmly hold on to another plant.
A rose plant which produces rose flowers has hooks which it uses to hook on to other plants as it grows.
A habitat is a place where a living organism lives.
Some plants use other plants as their home.
In most cases, the plants that are used as homes are also used as sources of nutrients by the parasitic plant.
Some fungi use other plants as homes.
Some live in cereals like maize and wheat.
Bug Habitat on Willow Plant

The nodules in leguminous plants are home to small living things, bacteria.
Unlike in parasitic plants, bacteria get a home and in turn change the nitrogen of the air into nitrates, food for the legume.
When the legumes die, the nitrates enter into the soil thus enriching the soil with nutrients for use by other plants.
If young green legumes are used as green manure, the nitrates are availed to all the plants as nutrients.
In some cases, two different plants, each of which cannot survive alone, may join together to form one organism.
An example is the lichen (a yellow-green dusty plant seen on tree barks).
One of the parts of lichen is a fungus that gives a home or habitat to the other smaller but green plants such as algae.
The algae are able to manufacture food by photosynthesis, some of which the fungi feeds on.
Some plants live or make a home under the shade provided by other plants.
The shade protects the plant from damage by intense sunlight. In the absence of such a shade or shelter, the plants that seek shade would die.
Examples of these plants are the mushroom and ferns.
4. Decomposition
When plants die, they rot or decay.
Rotting is also decomposition.
This is brought about by bacteria and fungi.
As they eat the dead plants to get nutrients to produce energy, bacteria and fungi change the huge dead plants into humus (the decaying organic matter) to be used by other plants.

Plants, therefore, depend on other plants to change them to humus when they die.
The interdependence can also be between plants and animals.
Animals and plants depend on each other for various reasons.
These reasons include:
(a) Food
Herbivores are animals that feed on plants.
Grazers are the herbivores that feed only on grass.
They include buffaloes, cows, and sheep.
Browsers are herbivores that feed only on plant eaves.
They include giraffes and goats.
Insectivorous plants on the other hand feed on animals (insects).
Examples of these plants are the Venus flytrap and the Pitcher plant.
(b) Air
Green plants make their food through photosynthesis, which requires carbon dioxide, water, sunlight, and chlorophyll.
During photosynthesis, the plants use carbon dioxide but release oxygen.
When animals eat food, they use the food eaten to release energy by burning the food in a respiration process.
Respiration uses oxygen and releases carbon dioxide.
Therefore, animals depend on plants to supply them with oxygen released during photosynthesis.
Likewise, plants need animals to release carbon dioxide to the environment, which they then use.
Food that is taken in by animals is used in the body to:
1. build new muscles, bones, blood cells, hair, nails, and other body tissues
2. repair worn-out body parts
3. provide energy for the body functions like circulation, breathing, and movement
4. To protect the body from diseases.
As food is used in the body, wastes are produced.
These wastes may also include the food that has not been digested.
The toxic wastes and undigested food must be removed from the body as waste matter.
Some of the wastes from animals can be converted into compost manure which has a lot of plant nutrients.
As such, animal wastes can be used as sources of nutrients by plants.
Animal waste can be made into compost, which then provides food nutrients in the form of minerals to plants.
Plants then make food from the water and minerals they absorb from the soil in the presence of carbon dioxide from the air, sunlight, and chlorophyll.
This food may be consumed by animals.
(e) Decomposition
When animals and plants die, their bodies are broken down into minerals by bacteria and fungi.
This process is decomposition and it helps in the formation of humus from the decaying organic matter which is essential for the proper growth of plants.
Plants provide shelter (home or habitat) to many animals such as birds, monkeys, chameleons, lizards, snakes, ants, caterpillars, and bees.
Cutting down of trees or destruction of bushes, therefore, means destroying animal habitats.
(g) Medicine
Human beings use some specific plants for medicinal reasons.
Different plants are used as herbal medicine by different communities for different illnesses.
The table below shows illnesses that are said to be cured by the specific plants shown.
Note: Green plants make their own food by the process of photosynthesis.
This food is made in the leaves and can be stored in various parts of the plant.
The food can be stored in the roots, stem or leaves.
Plants can therefore be classified according to how they store their food.
Examples of these classifications are:
Root tubers: these include carrots, cassava, and sweet potatoes.
They store their food in the swollen root.
Bulbs: examples of bulbs are the onion which stores its food underground.
The bulb contains the roots, flat stem and thick fleshy leaves.
Stem tubers: an example is the irish potato.
It is the swollen part of the stem that is found under the ground and it contains several buds (eyes).
Rhizomes: an example is the ginger.
It is an underground stem that grows horizontally.
Standard 7
1. The following flow chart shows some interrelationships between plants, animals, and soil.
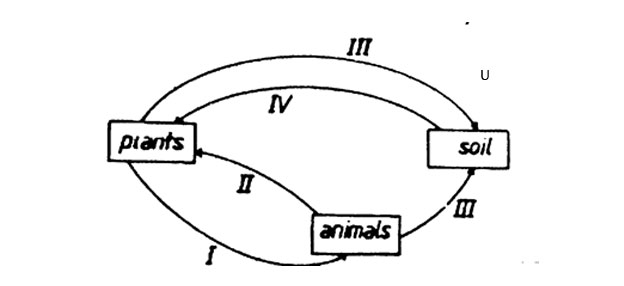
The arrows in the diagram above could represent.
|
I |
II |
III |
IV |
| A. Oxygen |
Carbon dioxide |
Decay |
Mineral salts |
| B. Carbon dioxide |
Oxygen |
Decay |
Mineral salts |
| C. Oxygen |
Carbon dioxide |
Minerals salts |
Decay |
| D. Mineral salts |
Oxygen |
Decay |
Carbon dioxide |
2. Below is a simple food chain.
Green plants -------> Small intestines -------> Large intestines---------> Small birds --------> Large birds
Note: The arrow points at the eater
In this food chain, what would be the effect of killing all the large insects?
A. Small insects would decrease.
B. Large birds would decrease.
C. Green plants would increase.
D. Small birds would increase.
3. The chart below shows part of the nitrogen cycle. Study it and answer the question that follows.
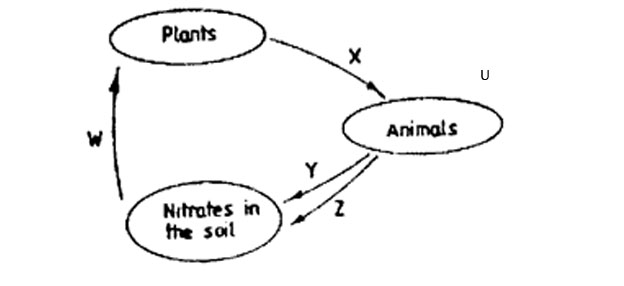
Which one of the following gives the correct processes represented by the arrows W, X, Y, and Z.
|
W |
X |
Y |
Z |
| A. Feeding |
Absorption |
Excretion |
Decaying |
| B. Absorption |
Decaying |
Feeding |
Excretion |
| C. Absorption |
Feeding |
Excretion |
Decaying |
| D. Feeding |
Absorption |
Decaying |
Excretion |
4. Study the diagram of the food web below and answer the question that follows.
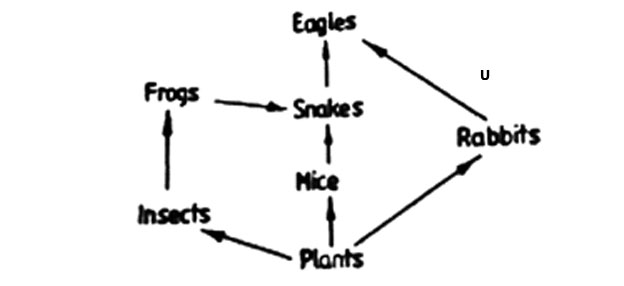
Which of the following animals should be most abundant in the food web?
A. Insects B. Snakes C. Frogs D. Rabbits
5. The function of the cup containing a liquid in the pitcher plant is to
A. Store excess food
B. Trap rainwater for the plant
C. Cool the leaves
D. Trap small insects
6. The chart below shows a feeding relationship in a certain habitat.
Grass -----> Insects -----> Lizards -----> Snakes
Note: The arrow points to the eater.
If a disease killed all the lizards, which one of the following would be the immediate effect?
|
Grass |
Insects |
Snakes |
| A. Decrease |
Increase |
Decrease |
| B. Increase |
Increase |
Decrease |
| C. Decrease |
Decrease |
Decrease |
| D. Increase |
Decrease |
Decrease |
7. Use the information below to answer the question that follows.
Frogs eat grasshoppers
Grasshoppers eat grass
Snakes eat frogs
From this information, which one of the following is the correct food chain?
A. Frogs – grasshoppers – grass – snakes
B. Snakes – frogs – grasshoppers – grass
C. Grass – grasshoppers – frogs – snakes.
D. Grass – grasshoppers – snakes – frogs
8. Which one of the following parts of an insectivorous plant is adapted for trapping insects?
A. Flower B. Leaf C. Stem D. Fruit
9. Susan studied feeding relationships among butterflies, owls and chameleons in a bush near her school. Which one of the following food chains CORRECTLY shows the relationship?
A. Owl – chameleons – nectar – butterfly
B. Owl – chameleon – butterfly – nectar
C. Nectar – butterfly – chameleon – owl
D. Nectar – butterfly – owl – chameleon
10. Which one of the following plants has nitrogen-fixing bacteria in its roots?
A. Millet B. Wheat C. Cassava D. Beans
11. The chart below shows a feeding relationship.
Fruits ----> Flies ----> Spiders -----> Chameleons -----> Hawks
N/B The chameleon also feeds on flies.
Which one of the following would happen if all the spiders died suddenly?
A. The population of chameleons would decrease
B. The chameleons will eat more flies
C. The chameleons would eat flies and fruits
D. The population of hawks would decrease