The flower is the reproductive part of the plant.
Functions of the flower:
• The stamen makes the pollen grains
• The pistil produces the ovules
• The flower allows for pollination.
• The ovary of the flower develops into a fruit after fertilisation.
• Fruits contain seeds.
Pollination is the transfer of pollen grains from the anthers to the stigma of the same type of flower.
There are two types of pollination:
self pollination and cross pollination.
Self pollination occurs when pollen from the anthers of a flower are transferred to the stigma of the same flower or a flower of the same plant.
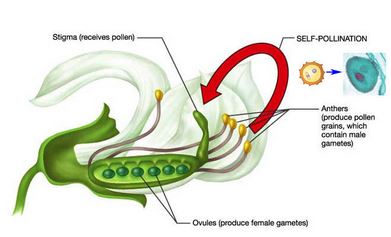

Cross pollination occurs when pollen from the anthers of one flower are transferred to the stigma of a flower on another plant of the same type by wind or insects.


Comparing wind pollinated flowers with insect pollinated flowers
|
Wind pollinated flowers |
Insect pollinated flowers |
|
Have small dull flowers |
Have large and brightly coloured flowers |
|
Have no nectar and no scent |
Produce nectar and often have strong scent |
|
The stigma is on a long stigma stalk |
Have a small but firm stigma so that it is exposed to the wind |
|
Produce small and smooth pollen |
Produce large sticky pollen |
|
Produce pollen grains |
Produce few pollen |
These are the things that help in pollination.
The agents of pollination include wind and animals for example insects and birds.
Plants pollinated by insects include hibiscus, beans and oranges.
If the insect enters into the flower, pollen grains stick to the insect.

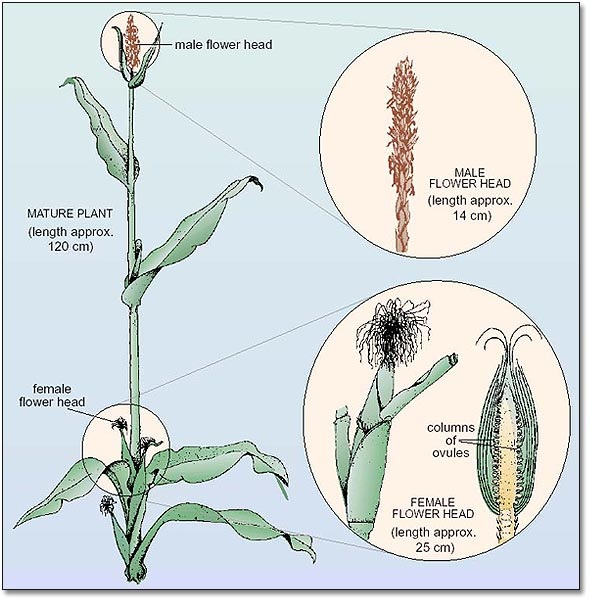
Examples of plants pollinated by wind are maize and grass
The tassel (male part) of a maize plant is at the top of the plant.
The cob (the female part) has silk-like threads which form the style and the stigma.
Within the cob, there are ovules.
The cob is usually below the tassel.
Grasses also have wind-pollinated flowers.
They have very small flowers, whose stigma is forked and hangs outside the flower.
The anthers also appear out of the flower, to release the pollen to the wind.
The stigma traps the pollen grains floating in the wind from different flowers.
Cross Pollination by Wind in Maize

When fertilisation takes place the following things happen:
1. The fertilised ovule becomes a seed containing an embryo.
2. The ovule wall becomes the testa or seed coat.
3. The ovary grows to become a fruit.
4. The ovary wall becomes the pericarp or fruit wall.
5. The flower withers and dies.

The seed is the fertilised ovule containing the embryo.
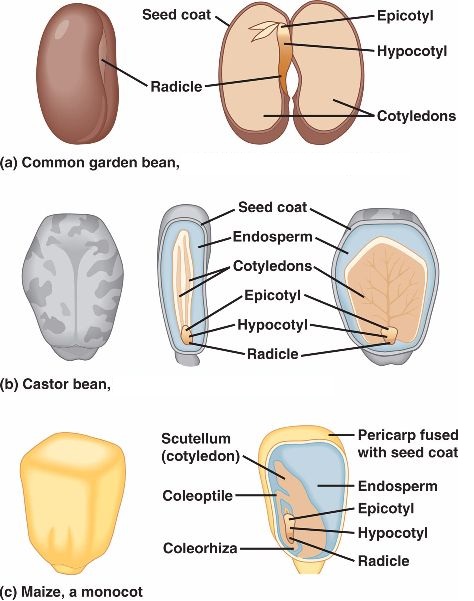
The embryo is made up of a plumule (later grows to be the shoot) and a radicle (later grows to be the root).
The embryo is usually covered by one or two cotyledons, which are stored food for the embryo (the tiny plant in the seed).
On the outside of the seed there is a scar the hilum, where the seed was attached to the fruit wall, and a small hole the micropyle.
Plants that produce seeds with one cotyledon are called monocotyledons.
Examples of monocotyledons are maize, barley, wheat, rice and millet.

Plants that produce seeds with two cotyledons are called dicotyledons.
Examples of dicotyledons are groundnuts, beans and castor oil.

Difference between seeds and fruits:
Seeds contains the embryo and its food store,
Seeds has a scar (hilum) where it was attached,
Seeds has a micropyle (a tiny hole for taking in water)
Fruits contains seeds in it.
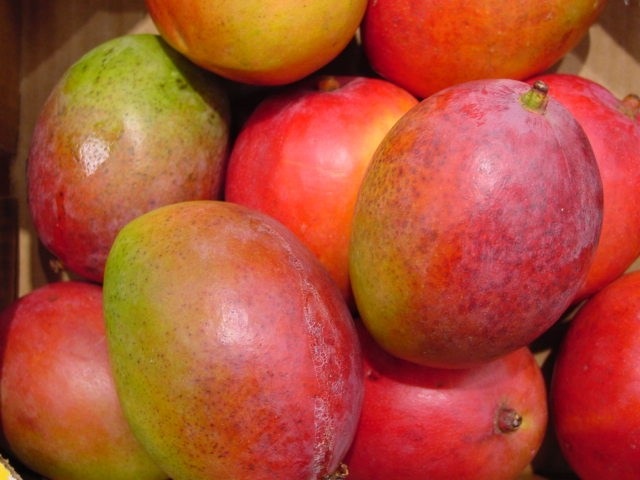
Fruits has two scars ;one where it was attached to the fruit wall to the flower stalk and the other where it was attached to the style,
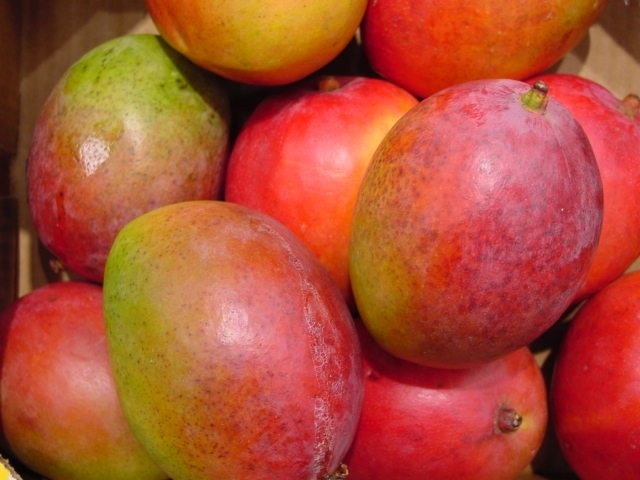

Get a mango fruit and observe the two scars mentioned above
When a seed starts to grow into a young plant we say it is germinating.
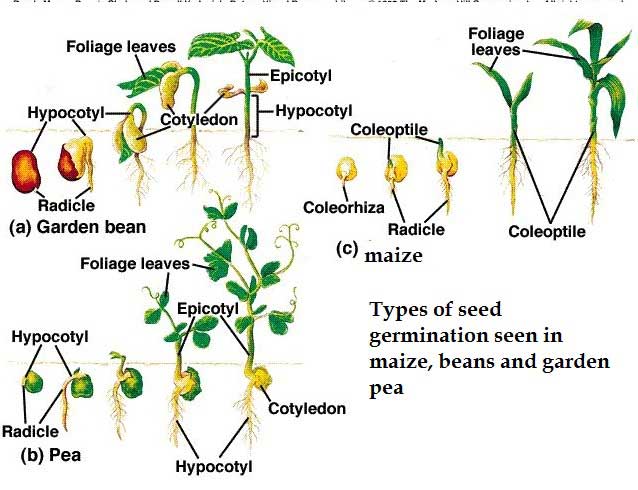
For a seed to germinate, the following conditions must exist:
1. There must be sufficient supply of water.
2. The temperature must be suitable. There must be enough warmth.
3. There must be air especially oxygen which is used by the embryo to break down stored food to give it energy.
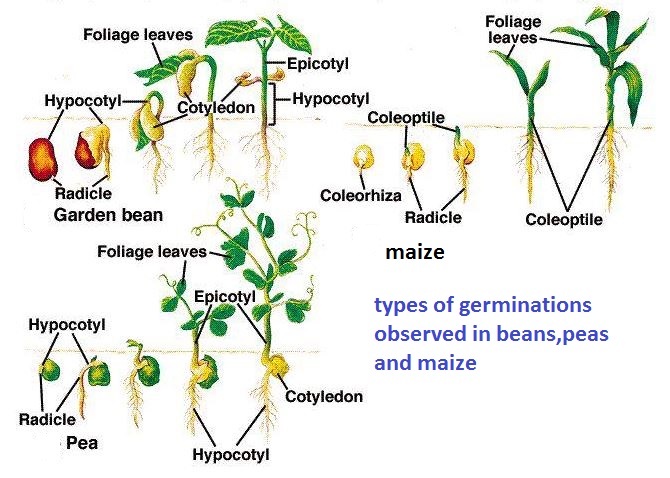
There are two types of germination namely:
Epigeal germination:
Hypogeal germination:
Standard 6
Study the diagram of the flower below and answer questions 1 & 2.
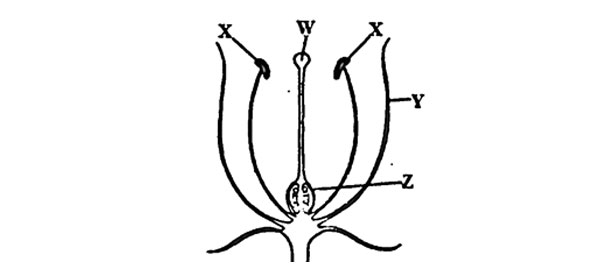
1. Which part of the flower develops into a fruit after fertilization?
A. W B. X C. Y D. Z
2. If the parts of the flower marked X were removed before they matured, which of the following statements would be correct?
A. Pollen grains will not be produced
B. Fertilization can never take place
C. Ovules will not be formed
D. The flower will not attract insects
3. The information in the table below is about flowers labeled E, F, G and H
|
Flower |
Characteristics |
|
E |
Large petals, has nectar |
|
F |
Large amount of pollen, loosely attached anthers |
|
G |
Red in colour, strong scent |
|
H |
Anthers outside the flower, feathery stigma |
Which one of the following pair of flowers are insect pollinated?
A. E and F B. G and H C. H and F D. E and G
4. The main difference between fruits and seeds is that fruits
A. Are edible but seeds are not.
B. Have two scars but seed have one.
C. Have bright colours but seeds are dull.
D. Are large but seeds are small.
5. Standard V pupils at Fulani Primary school measured the amount of rainfall for each month of the year and repeated the measuring for several years. They recorded the averages of their measurements in the table as shown below.
|
Month |
Jan |
Feb |
Mar |
Apr |
May |
Jun |
July |
Aug |
Sep |
Oct |
Nov |
Dec |
|
Average rainfall (per month mm) |
29 |
49 |
117 |
306 |
179 |
47 |
19 |
24 |
30 |
112 |
180 |
176 |
Which pair of months would be the most appropriate for planting maize around Fulani primary school?
A. July and December
B. February and July
C. February and September
D. September and December
6. Which one of the following processes in plants is correctly matched with its meaning.
|
Process |
Meaning |
| A. Transpiration |
Loss of water from the leaves to the atmosphere |
| B. Respiration |
Combination of water and carbon-dioxide to produce food. |
| C. Pollination |
Joining of pollen grains |
| D. Fertilisation |
Transfer of pollen grains from anthers to stigma |
7. The diagram below represents the parts of a bean seed. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follows.
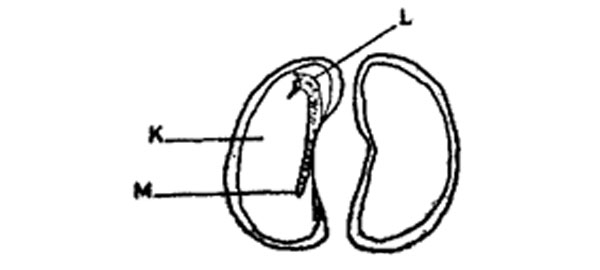
Which one of the following gives the correct functions of the parts labelled K, L and M?
|
K |
L |
M |
| A. Protects the seed |
Stores food |
Develops to a shoot |
| B. Stores food |
Develops to a shoot |
Develops to a root |
| C. Allows water in |
Develops to a shoot |
Develops to a root |
| D. Stores food |
Allows water in |
Develops to a shoot |
8. In which one of the following parts of a flower does the pollen tube develop?
A. Filament B. Petal C. Style D. Anther
9. Which one of the following is NOT necessary for the germination of seeds?
A. Warmth B. Oxygen C. Moisture D. Light
10. The diagram below represents a flower opened to show inner parts.
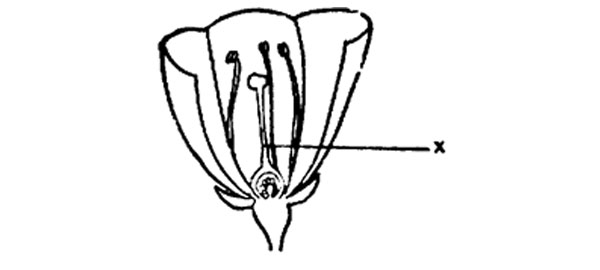
The part marked X is the
A. Stamen B. Filament C. Stigma D. Style
11. A section through a maize grain is shown in the diagram below.
[resource: 8395, align: left]
The part marked P is the
A. Radicle B. Hilum C. Cotyledon D. Plumule
12. A section through a bean seed is shown in the diagram below.
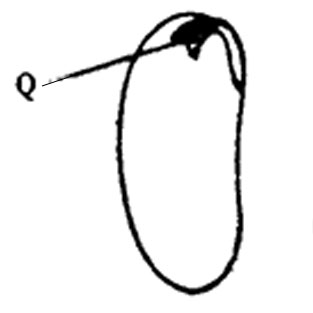
The part labeled Q is the
A. Hilum B. Plumule C. Radicle D. Cotyledon
13. Which one of the following parts of a flower is correctly matched with its function?
|
Part |
Function |
| A. Stigma |
Produces pollen grains |
| B. Petals |
Attract insects |
| C. Anther |
Receives pollen grain |
| D. Style |
Holds the anther |
14. Which parts of a maize grain remain underground after germination?
A. Plumule and radicle B. Cotyledon and plumule
C. Food store and plumule D. Radicle and food store
15. The diagram below represents an insect-pollinated flower cut to show the inner parts.
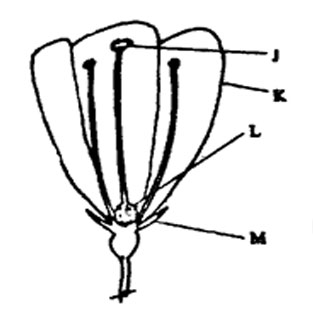
The part of the flower which attracts insects is
A. J B. K C. L D. M
16. Which one of the following characteristics of flowers is found in wind-pollinated flowers only?
A. Brightly coloured petals B. Scented nectaries
C. Feathery stigma D. Large flower parts
17. Which one of the following plants is non-flowering?
A. Mushroom B. Grass C. Cactus D. Onion
18. Which one of the following statements would be true about a young insect-pollinated flower whose styles have been cut off?
A. Pollen grains would not develop
B. Pollination would occur
C. Ovules would not develop into seeds
D. Anthers will not produce pollen.
19. Standard five pupils planted seeds in a container. After germination, they added water that covered the seedlings. They then placed the container outside the classroom. They noted that the seedling died after a few days.
The main reason why the seedlings died was due to
A. Too much light.
B. Lack of air.
C. Lack of warmth.
D. Lack of mineral salts.
20. Why is it recommended to water seedlings in the mornings and evenings instead of watering them early in the afternoon?
A. Seedlings absorb moisture faster in the mornings and evenings.
B. There is less moisture loss in the mornings and evenings.
C. Seedlings require more water in the mornings and evenings.
D. Seedlings grow faster when watered in the mornings and evenings.
21. Which one of the following characteristics of a maize plant DOES NOT help its pollination?
A. Smooth and light pollen grains
B. Feathers-like styles.
C. Colour of the flower.
D. Stigmas which hand out of the flower
22. Standard Eight pupils carried out experiments to find out the conditions necessary for germination. They placed been seeds in water which had been boiled, covered with oil and cooled room temperature.
The seeds did not germinate because they lacked
A. Oxygen B. Light C. Warmth D. Soil
23. The table below shows the features of four different types of flowers.
|
Flowers |
Features |
|
P |
Anthers only |
|
Q |
Stigma sticking outside |
|
R |
Stigma longer than the anthers |
|
S |
Stigma shorter than the anthers |
Which one of the flowers is most likely pollinated by wind?
A. P B. Q C. R D. S
24. The diagram below represents the external structure of a bean seed.
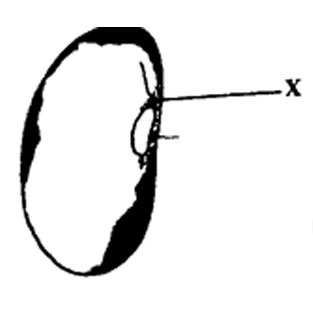
The part labeled X is called
A. Hilum B. Plumule C. Micropyle D. Radicle
25. Juma wanted to investigate the conditions necessary for seed germination. The set-up is shown in the diagram below.
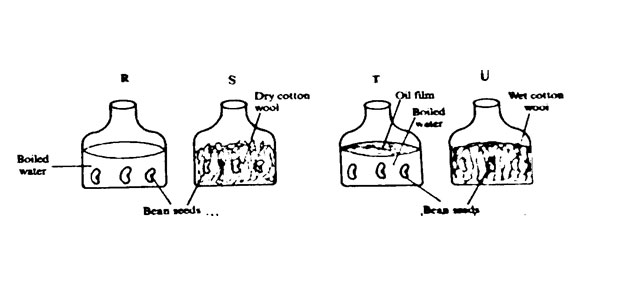
Which pair of set-up will enable Juma to make the conclusion that moisture is necessary for seed germination?
A. R and S B. R and T C. S and U D. T and U