Heat is a form of energy that we feel as temperature.
Heat can be felt as warmth or hotness.
Lack of it is felt as cold.

Anything that produces warmth is referred to as a Source of heat.
Examples of common sources of heat are the sun, fire, electricity, and gas.

We can put heat into many uses in our daily lives.
We can use heat for:

Heat travels from hotter areas to cooler areas (from a hot place to a cold place).
The movement of heat from one place to another is called heat transfer.
Heat transfer can take place in three ways:
This is the movement of heat through solids.
When you hold a rod of metal on one end and place the other end above a source of heat, after some time you will feel the heat on your hand from where you are holding the metal.
The heat travels from one end of the metal to the end where your hand is through conduction. Some materials transfer heat faster than others.
These materials are called Good conductors of heat.
An example of a good conductor of heat is a metal such as copper.
Materials that do not transfer heat are called poor conductors of heat.
Examples are wood and glass.
This is the movement of heat through FLUIDS (liquids and gases).
When water is heated in a sufuria, the water near the bottom of the sufuria becomes heated first.
When the water becomes hot, it rises up to the top of the sufuria.
As it does this, the cold water at the top of the sufuria moves down to the bottom of the sufuria, where it is heated too.
After some time all the water in the sufuria is heated through convection.
This is the movement of heat from one part of a surrounding to another part without the use of any material or medium.
Heat from the sun reaches the earth's surface through radiation.
When a jiko is lit and placed in one corner of a room and you sit at another corner, heat will reach you from the jiko through radiation.
Watch the video below
1. Some standard VI pupils poured equal volumes of boiling water at the same time into three cups as represented by the diagrams below:
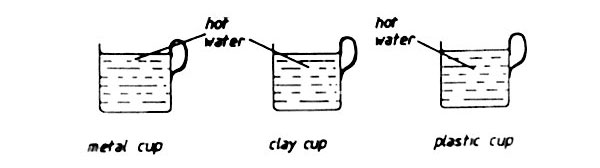
They then left the cups on the desk for 10 minutes and measured the temperature of the water in each cup. If the cups were all the same size, colour, thickness and shape, which one of the following statements is MOST likely to be correct?
The temperature of the water in
A. The metal cup was the lowest B. All the cups was the same
C. The clay cup was the lowest D. The plastic cup was the lowest
2. A pupil heated water in a container as shown in the diagram below. Select from the following the main method by which heat travels from point P to point Q.
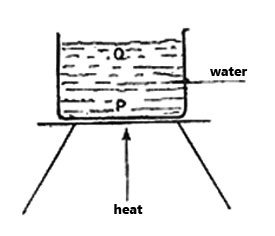
A. Conduction B. Convection C. Radiation D. Expansion
3. The diagram below shows water in a container being heated.
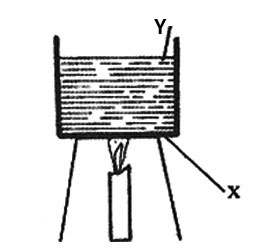
Heat is transferred from point X and Y by
A. Conduction and convection
B. Conduction and radiation
C. Convection and radiation
D. Convection and conduction
4. Ali obtained two identical containers. He painted one black and the other white. He then put equal amounts of water in the two containers and left them in the sunshine for the same length of time. Which of the following statements about the water is TRUE? The temperature of the water in the
A. Two containers would be equal.
B. White container would be higher than that in the black container.
C. Black container would be higher than that in the white container.
D. Two containers would not change.