| The Arms of government |
|---|
| Assessment Questions |
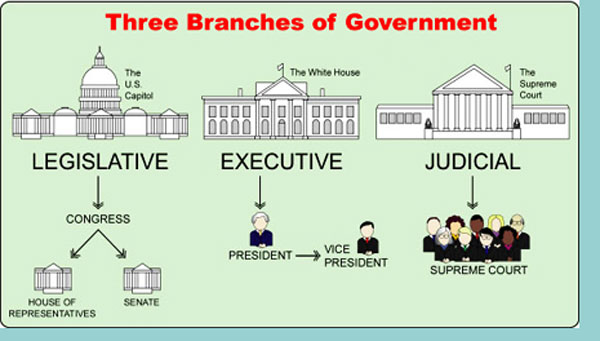
The Arms of government are:
Play the video below:
- The Legislature consists of the National Assembly and the Senate.
- The image below shows the current state of the two;
In the constitution, the National Assembly comprises:
A view from the inside of the National Assembly

Functions of the National Assembly
1. To determine the allocation of national revenue between the different levels of government.
2. To make and amend laws that govern the people of Kenya.
3. To deliberate on and resolves issues of concern to the people.
4. To represent the people in the constituency and their interest to the national assembly.
5. To approve declarations of war and extensions of state emergency.
6. To approve or disapprove presidential appointees.
7. To review the conduct in the office of the President, the Deputy President, and other State officers and initiates the process of removing them from office; and exercises oversight of state organs.
8. To exercise oversight over national revenue and its expenditure.
9. To appro[riate funds for expenditure by national government and other national state organs.
This part of the parliament consists of:
It has a total of 68 members.
See the representation below:
Functions of the Senate
1. To represent the counties, and serves to protect the interests of the people in the counties and the county governments.
2. To participate in the law-making function of Parliament by considering, debating and approving Bills concerning counties.
3. To determine the allocation of national revenue among counties, as provided and exercise oversight over national revenue allocated to the county governments.
4. The Senate participates in the oversight of state officers by considering and determining any resolutions to remove the President or Deputy President from office in cases of gross misconduct.
This arm consists of:
See the image below:
a) The President
i) The president is elected by registered voters in a national election. An election of the President is held on the same day as a general election of Members of Parliament.
ii) The President is the head os state and government. He exercises the executive authority of the republic, with the assistance of the Deputy President and Cabinet Secretaries.
iii) The President is the Commander-in-Chief of the Kenya Defence Forces. He is the chairperson of the National Security Council and is a symbol of national unity.
Functions of the president
1. The president addresses the opening of each newly elected parliament.
2. He or she also address a special sitting of parliament once every year.
3. The president also reports, in an address to the nation, on all the measures of the national taken and the progress achieved in the realization of national values.
4. The President nominates and, with the approval of the National Assembly, appoints, and may dismiss: the cabinet Secretaries, the attorney general, the Secretary to the Cabinet, Principal Secretaries, High commissioners, ambassadors, and diplomatic and consular representatives.
5. The President chairs the Cabinet meetings.
6. The President directs and co-ordinates the functions of ministries and government departments
7. The president receives foreign diplomats and consular representatives.
8. President pardons convicted criminals.
9. Confers honours and national awards in the name of the people and the republic.
10. Declares a state of emergency and with approval of parliament, declares war.
11. The President shall ensure that international obligations of the republic are fulfilled through the actions of the relevant Cabinet Secretaries.
12. The President assents to bills passed by Parliament for implementation.
b) The Deputy President
1. Each candidate in a presidential election nominates a person who is qualified for nomination for election as President, as a candidate for Deputy President.
2. The Deputy President it the principal assistant of the president and deputies for the President in the execution of the President's functions.
Functions of the Deputy President
1. The Deputy President is the principal assistant of the President and deputizes for the President in the execution of the President's functions.
2. The Deputy President performs the functions conferred by the Constitution and any other functions of the President may assign.
3. With the absence of the President or is temporarily incapacitated and during any period that the President decides, the Deputy President acts as the President.
c) The cabinet
The cabinet consists of:
i) the President
ii) the Deputy President
iii) the Attorney-General
iv) Cabinet Secretaries ( not fewer than fourteen and not more than twenty-two)
Functions of the Cabinet
1. Provides parliament with reports.
2. Manages the various government reports
3. Cabinet Secretaries formulate government policies.
4. Advises the president in the running of the government.
5. The Cabinet Secretaries are the chief accounting officers of the ministries.
6. The Attorney General is the Legal Advisor of the government.
7. The Attorney General represents the national government in any legal proceedings to which it is a party.
The Judiciary consists of the judges of the superior courts, magistrates, other judicial officers, and staff.
There is also the office of:
The court system of Kenya is classified into two;
1. The superior courts which include:
2. The subordinate courts which include:
The Supreme Court
The Supreme Court consists of:
Functions of the Supreme Court
The image below shows :

The Court of Appeal consists of twelve or more judges.
It is headed by the president of the Court of Appeal elected by the judges of this court from among themselves.
The function of this court is to hear appeals from the High Court and any other court or tribunal.
The High Court has several judges.
It is headed by the Principal Judge who is elected from among the judges of this court.
An image showing the High court in session:
The functions of the High Court;
These courts handle civil and criminal cases.
See the image below:
These courts deal with disputes among Muslims especially on marriage and inheritance issues.
This handles disciplinary cases of the officers of the Defence Forces.
In exercising judicial authority, the courts and tribunals serve the following functions: