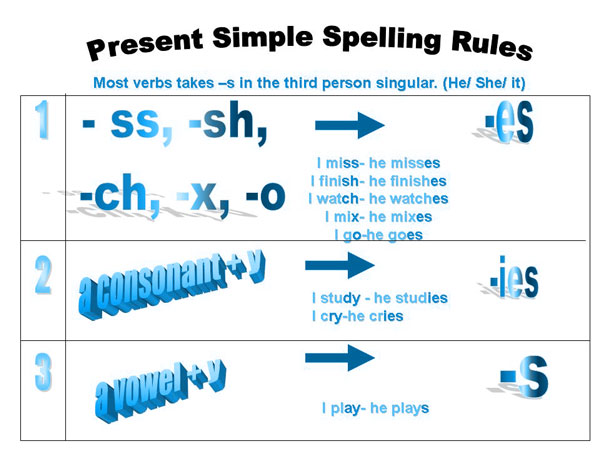
Tenses
Tense
Tense in writing deals with the relationship between an action of the verb and when the action is taking place.

An action may take place in the past, present or future.
The tenses may be summed up as follows:
1. Present Tense
(i) Simple present tense
- I drink tea every afternoon.
- We drink tea every afternoon.
Note
(ii) Present continuous tense
- He is painting the room.
- They are painting the room.



(iii) Present perfect/participle tense
- She has swept the compound clean.

2. We have swept the compound clean.

(iv) Present perfect continuous tense
- The teacher has been marking composition.

2. The teachers have been marking composition.
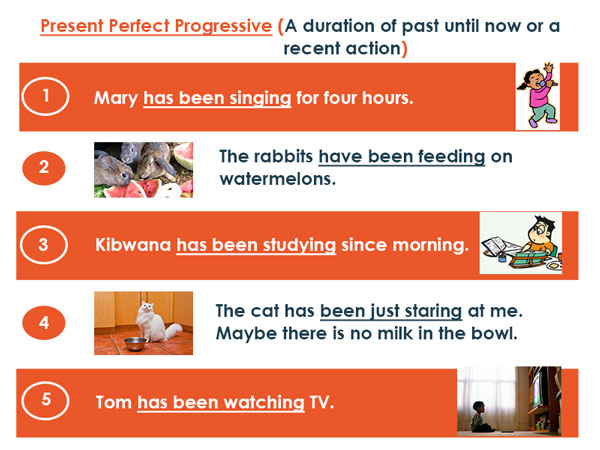

You can use short form or long form like the example below

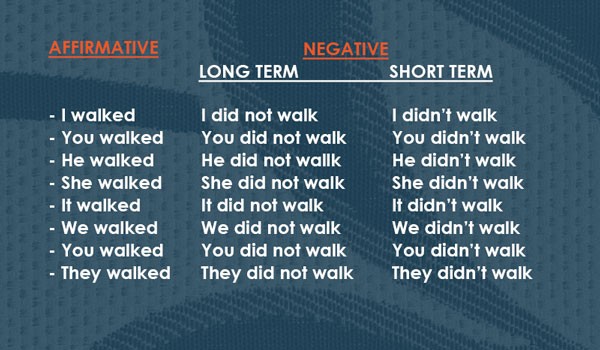
2. Past Tense
(i) Simple past tense
- John kicked the ball across the field.

2. The players kicked the ball across the field.
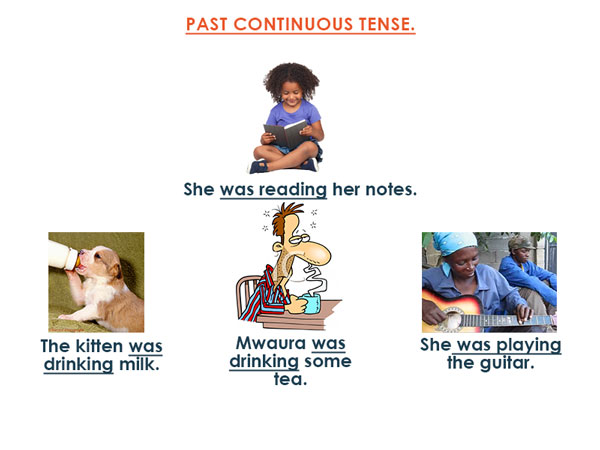
(ii) Past continuous tense
- The monkey was climbing the tree.

2. The monkeys were climbing the tree.
(iii) Past perfect tense
- Mother had forgotten her parcel.
- The people had forgotten their parcels.

(iv) Past perfect continuous tense
- The chief had been looking for the culprit.

2. The policemen had been looking for the culprit.
3. Future Tense
(i) Simple future tense
- I shall visit Mombasa next August holiday.
- We will visit Mombasa next August holiday.

(ii) Future continuous tense
- The villager will be cooking for the visitors.

2. The villagers will be cooking for the visitors.
(iii) Future perfect tense
- The landlord will have renovated the house.
- The landlords will have renovated the houses.

(iv) Future perfect continuous tense
- The tourist will have been visiting Kenya severally.
- The tourists will have been visiting Kenya severally.