Sentences are the building blocks of our language
The 2 Main Parts are:
Subjects
Predicates

A subject is the noun.
A predicate is a part of a sentence containing a verb that makes a statement about the subject of the verb.
The Subject is the Noun of the sentence, The sentence is also based upon the Noun
In, “The beautiful dancer leaped into the air like a deer.” Dancer is the subject

The quickest way to find the subject is to read the sentence carefully
The subject can be singular or plural and 1 or 2 words
In long sentences, once you identify the subject, the rest of the sentence is the predicate.
The beginning of the predicate is a verb.
Example

The predicate names the verb in the sentence that tells what is happening
In, “The beautiful dancer leaped into the air like a deer.” leaped is the predicate
The easiest way to find the predicate is to find what the subject is doing
SCHOOL

Vocabulary to Use in This Section
advise, certificate, anthem, greetings, mathematics, social studies, punctuation
marks, full stop, question mark, capital letters, monitor, prefect, homework, always, went, wait for, hardly, classmates
Sentence structure using the vocabulary given above;
The class prefect shouted that it was mathematics time.
Class prefect is the subject
shouted that it was mathematics time is the predicate
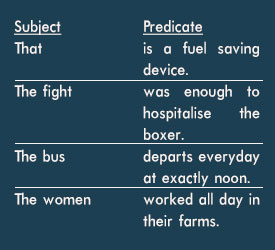
A complete sentence must have a subject and a predicate.
The subject tells who or what does the action, and the predicate contains the verb and tells what the action is.

A verb is a word that expresses one of two things:
Action: jump, scream, fly, run
State of being: appear, seem, feel
A subject can be any of the following things:
1. The person who does the action in the sentence.
Grandpa sells goods in his general store.
2. The place that does the action in the sentence.
The general store swarms with people before the Fourth of July celebration.
3. The thing that does the action in the sentence.
Flour and sugar are mixed together to make cookies.
4. The person described in the sentence.
Grandpa is happy when he makes a good sell.
5. The place being described in the sentence.
The general store is crowded on Saturday.
6. The thing being described in the sentence.
Cookies are best when the flour and sugar are fresh.
Subjects may come in different forms
One noun as the subject – Billy wants hound dogs.
Two nouns as a subject – Little Ann and Old Dan are two dogs.
One pronoun as the subject – He prays each night for dogs.
Two pronouns as the subject – He and she are both still awake because of the coon hounds.
A phrase – Staying awake all night is no fun.
A clause – What makes me mad is all the noise!
Clause
when he gets the money
(This has a subject [he] and a verb [gets], but you’re left wondering, aren’t you?
It’s not a complete sentence.
This is called a dependent clause.

It depends on something else to make a complete sentence.
Complete Sentence
Billy will buy textbooks when he gets the money.
(Now we know what’s going on!)

Watch this video about subject and predicate










